Search
Meet the directors and researchers that make up the team behind ORIGINS.
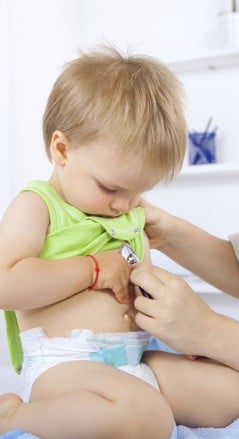
Developmental Origins of Health and Disease
See the latest ORIGINS news.

ORIGINS has secured $500,000 in funding from the WA Government’s Future Health Research and Innovation (FHRI) Fund.

Read our contribution to Research Australia's INSPIRE magazine in their 'Prevention' edition.

This article explores how to support a child's physical and mental health during critical developmental periods, known as the first 1,000 days of life.
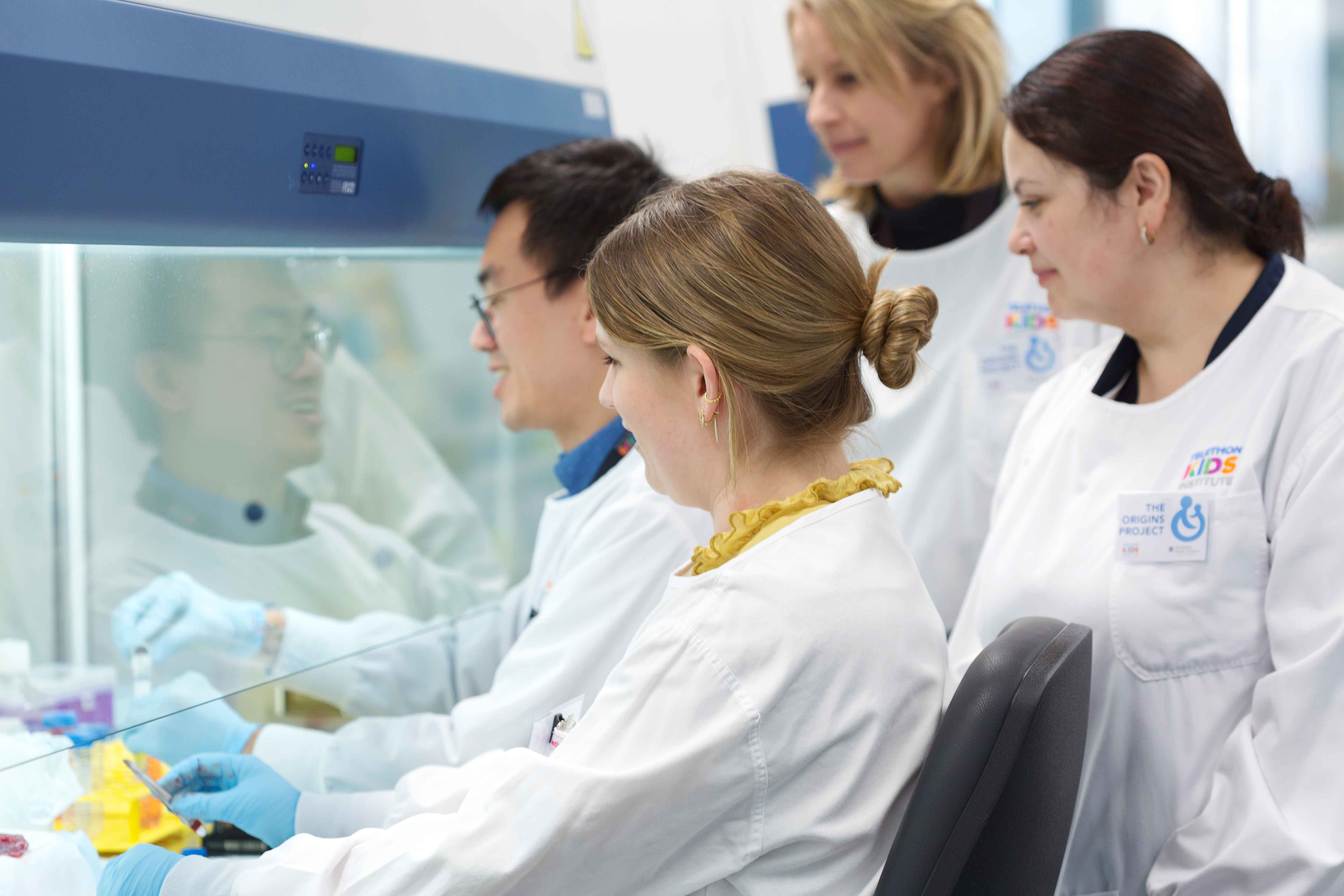

What if researchers could shop for different data to help uncover how, when and why chronic conditions such as asthma, obesity, allergies and poor mental health develop?

ORIGINS Co-Director nominated in the 2024 Western Australian of the Year Awards

ORIGINS Study publishes protocol

Ground-breaking WA-led study, Early Moves has hit a major milestone, with 3,000 participants successfully recruited over a four-year period.
