Search
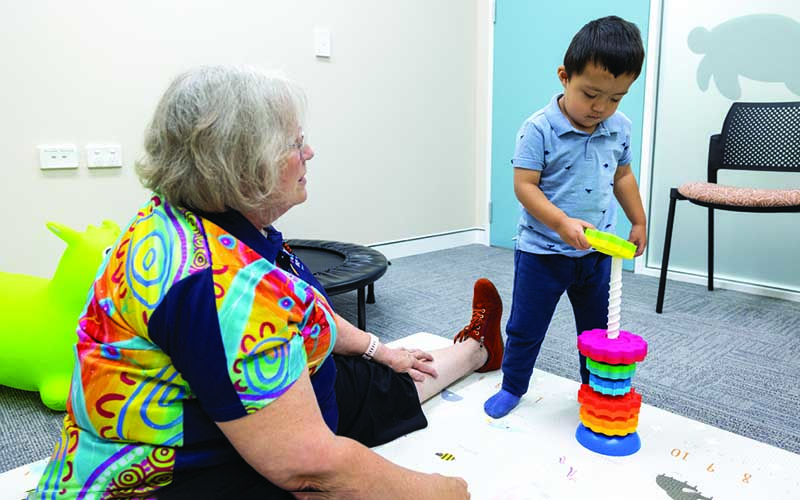

Discover how this family is benefitting from CliniKids' evidence-based therapies.

In this blog, Curtin University Occupational Therapy students Julia Walker and Mandy Bull delve into the history of Occupational Therapy in Australia.
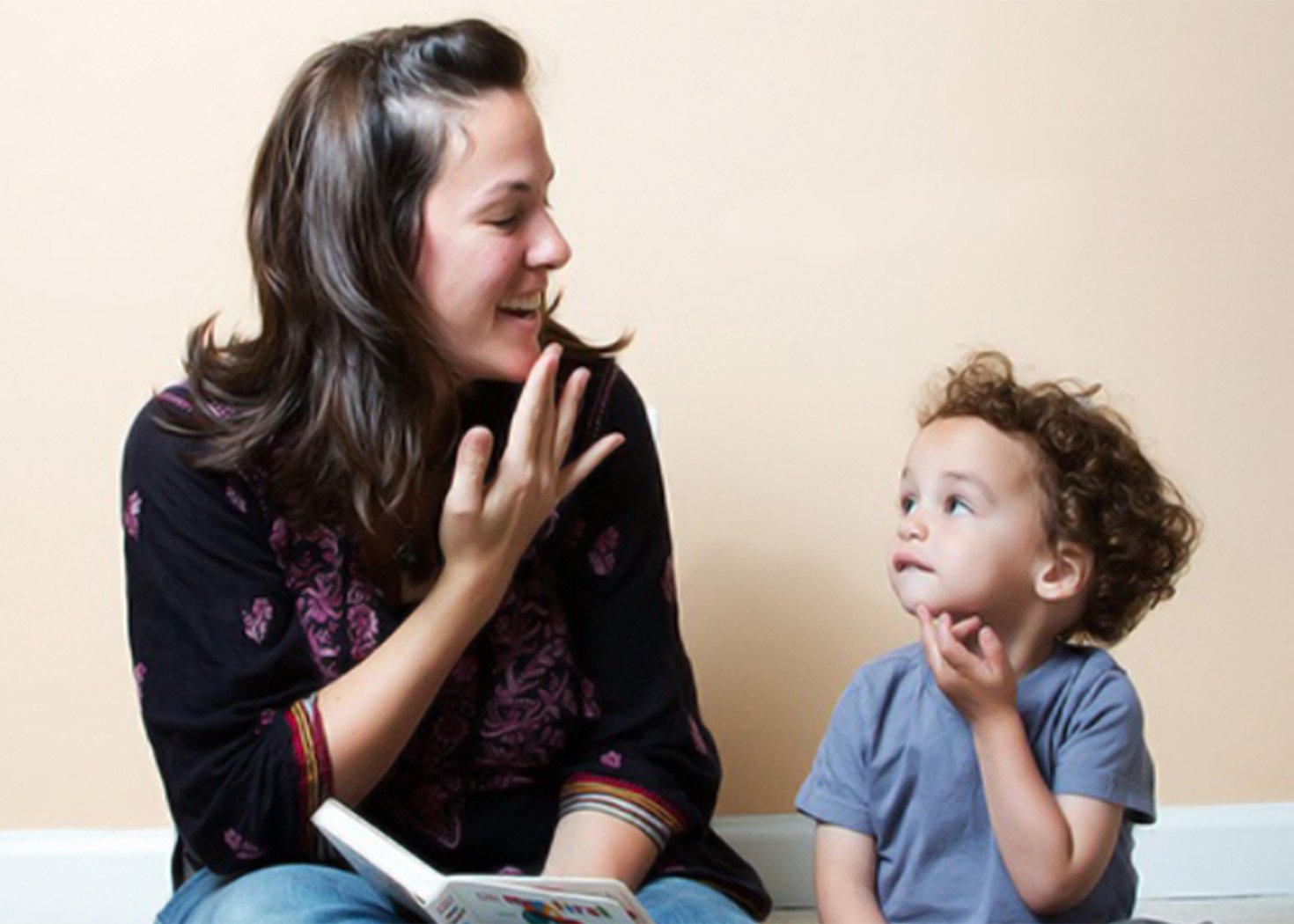

In this new blog, Senior Speech Pathologist Marisa Di Lorenzo discusses Augmentative and Alternative Communication and how it supports every individual’s access to the basic right of communication.
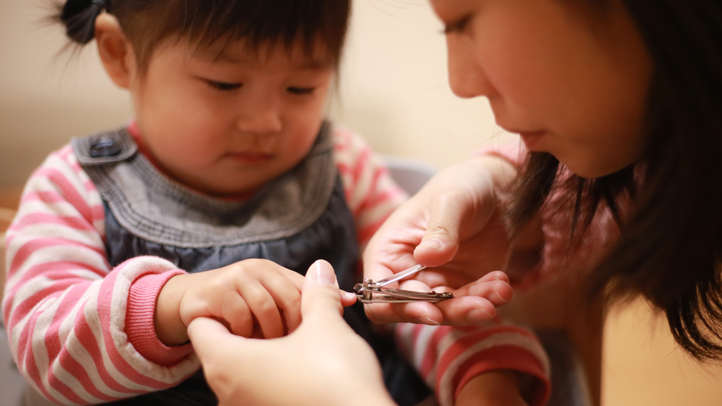

In this blog, Curtin University Occupational Therapy student Julia Than discusses how to make nail care an important part of a child's self-care routine.
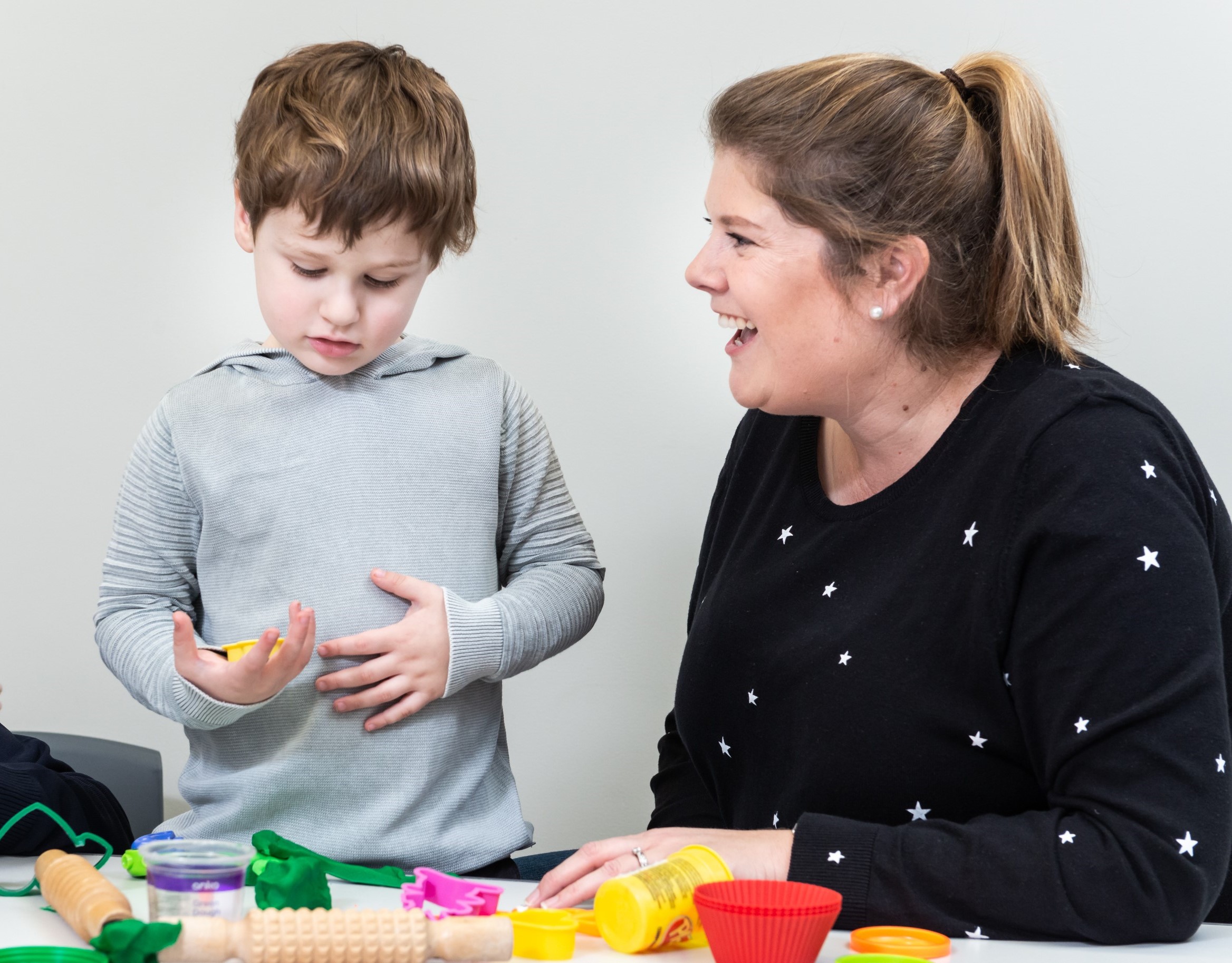

In this new blog, Senior Speech Pathologist and PACT therapist/trainer Sally Grauaug discusses the benefits of PACT, how it works and how clinicians become certified PACT therapists.

In this blog, Therapy Assistant and JASPER Practitioner Storme-Louisa Will offers some tips for promoting authentic and enjoyable play.
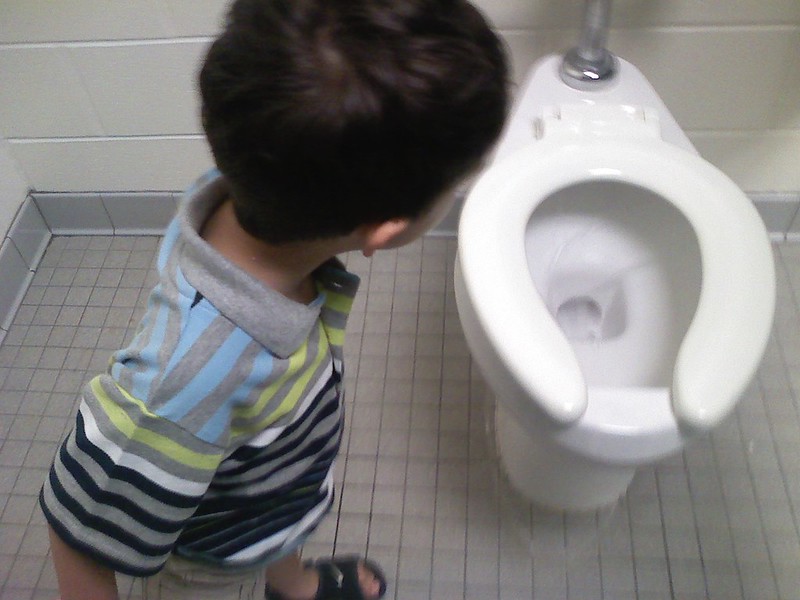
In this blog, Occupational Therapist Ally Raphael offers tips for successful toilet training.

In this blog, Speech Pathology Clinical Lead Aria May looks at telehealth and how it can support children and families with their therapy goals.

Professor Andrew Whitehouse recently spoke with ABC Perth’s Geoff Hutchison and Andrea Burns, Postgraduate Broadcasting Academic at ECU, for their ‘What Just Happened?’ segment which involves sitting down with a prominent Perth figure to get a sense of their life story and what matters most to them.

In this blog, Speech Pathology Clinical Lead Aria May discusses serve and return interactions to promote connection and communication with your child.
