Search

Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Mitigates the Inhibition of Airway Epithelial Cell Repair by Neutrophil Elastase Abstract Neutrophil elastase (NE) activity is

Interleukin-1 is associated with inflammation and structural lung disease in young children with cystic fibrosis Early diagnosis and treatment in

Single-breath washout and association with structural lungdisease in children with cystic fibrosis Abstract Background: In children with cystic

Effect of Posture on Lung Ventilation distribution and Associations with Structure in Children with Cystic Fibrosis Effect of Posture on Lung
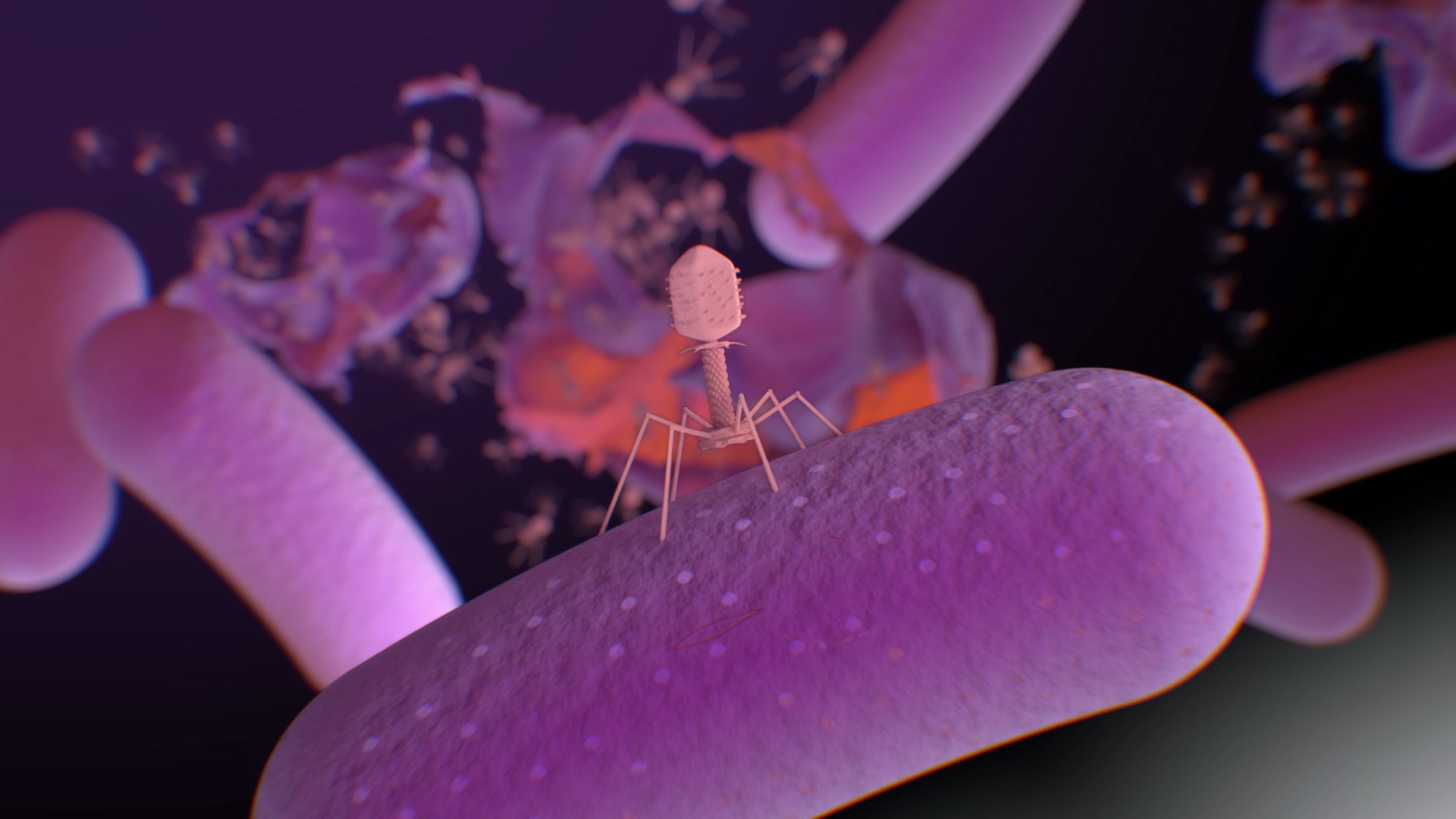
START Phage WA was formed to pave the way towards treating AMR infections with phage therapy in Western Australia.

Community involvement plays an integral role in guiding our research - find out how.

The Western Australian Epithelial Research Program (WAERP) is a community cohort biobank that collects and stores airway cells from the upper (nose) and lower (trachea) airways of Western Australian children and adults (1-50 years of age) undergoing non respiratory elective surgery.

The Western Australian Epithelial Research Program (WAERP) biobank is undertaking a number of research projects intended to improve the understanding and preclinical assessment of therapeutics for respiratory conditions.
Research
DETECT Schools Study Protocol: A Prospective Observational Cohort Surveillance Study Investigating the Impact of COVID-19 in Western Australian SchoolsAmidst the evolving COVID-19 pandemic, understanding the transmission dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 virus is key to providing peace of mind for the community and informing policy-making decisions. While available data suggest that school-aged children are not significant spreaders of SARS-CoV-2, the possibility of transmission in schools remains an ongoing concern, especially among an aging teaching workforce. Even in low-prevalence settings, communities must balance the potential risk of transmission with the need for students' ongoing education.
Research
An observational study of antibody responses to a primary or subsequent pertussis booster vaccination in Australian healthcare workersAdult pertussis vaccination is increasingly recommended to control pertussis in the community. However, there is little data on the duration and kinetics of immunity to pertussis boosters in adults. We compared IgG responses to vaccination with a tetanus, low-dose diphtheria, low-dose acellular pertussis (Tdap) booster at 1 week, 1 month and 1 year post-vaccination in whole-cell (wP)-primed Australian paediatric healthcare workers who had received an adult Tdap booster 5-12 years previously, to those who received their first Tdap booster. Tdap vaccination was well tolerated in both groups.
