
Britta Regli-von Ungern-Sternberg AM FAHMS
Chair of Paediatric anaesthesia, University of Western Australia; Consultant Paediatric Anaesthetist, Perth Children’s Hospital; Head, Perioperative Medicine
MD, PhD, DEAA, FANZA
Professor Britta Regli-von Ungern-Sternberg, leader of the Perioperative Medicine Team, holds the foundation Chair of Paediatric Anaesthesia at the University of Western Australia (the first of its kind in Australasia), and is a specialist paediatric anaesthetist at Perth Children’s Hospital. She leads the most active paediatric anaesthesia research program in Australasia which is also an internationally leading program focusing on continuously driving improvements in safety and quality of care along the perioperative pathway. The research team is strengthened by its multidisciplinary nature comprising anaesthetists, surgeons, physicians, nurses, allied health professionals, engineers, scientists, statisticians and health economists across multiple medical and academic institutions. These diverse clinical networks provide strong evidence for immediate translation into tangible health benefits for young Australians.
Her main research interests relate to the prediction and prevention of respiratory complications in paediatric anaesthesia, lung function changes during anaesthesia, the evaluation of different airway devices, as well as the impact of anaesthesia in early life on a child’s neurodevelopment.
Britta was appointed to the Clinical Senate of Western Australia (2020-2022) and sits on the Scientific Advisory Safety Committee of the Child and Adolescent Health Service Human Research Ethics Committee. She is a member of the Executive for the Clinical Trials Network of the Australia and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists (ANZCA) as well as a member of the ANZCA Research Committee and sits on the Society for Paediatric Anaesthesia Research Committee. She is a Section Editor and Editorial Advisory Board member for the journal Pediatric Anesthesia.
Published research
Taste-Masked Diclofenac Sodium Microparticles Prepared by Polyelectrolyte Complexation: Formulation Using Different Fatty Acids and Taste Evaluation by Human Panel
Paediatric patients continue to lack access to age-appropriate oral medicines for their treatment and have to depend on the off-label use of medicines approved for adults, which compromises dosing accuracy and exposes children to unpleasant bitterness.
Improving Outcome Reporting in Paediatric Airway Management in Clinical Trials (IMPACT): A Study Protocol for Core Outcomes and Clinical Endpoints
Although clinical trials are fundamental to advancing evidence-based practice, significant heterogeneity in outcome reporting poses a considerable challenge to the validity of systematic reviews. This inconsistency impedes the ability to compare, synthesise and interpret research findings effectively. In the field of paediatric airway management, this issue is particularly relevant because of the low incidence of critical events and the related high morbidity and mortality. The issue of inadequate and variable outcome reporting in clinical trials has been widely acknowledged, necessitating initiatives to enhance the quality of future research.
Pain and recovery profiles following common orthopaedic surgeries in children
Little evidence exists on the postoperative trajectory after paediatric orthopaedic surgery. Pain and behavioural disturbance can have short- and long-term impacts on children and their families. An improved understanding of procedure-specific postoperative trajectories can enhance recovery. The primary outcome was to examine the duration and severity of postoperative pain experienced by children undergoing 10 commonly performed orthopaedic procedures.
Numerical simulation of aerosolised medicine delivery through tracheostomy airways
The administration of inhaled antibiotics to patients with upper or lower respiratory infections is sometimes conducted via a tracheostomy airway. However, precise dosing via this route remains uncertain, especially in spontaneously breathing paediatric patients.
Impact of pediatric anesthesia management on cancer outcomes in children—a narrative review
The relationship between anesthetic technique and pediatric oncological outcomes is an emerging field of interest. With significant improvements in childhood cancer survival in recent decades, there is an increased focus on optimizing the quality of survival and reducing the incidence of metastasis and recurrence. The aim of this narrative review article is to investigate and consolidate the current available evidence assessing the immunomodulatory effects of anesthesia in the pediatric oncology population.
Trends in paediatric anaesthesia research publications and the impact of author sex, country of origin, topic, and external funding
The current research landscape has become increasingly competitive with approximately 35% of submitted manuscripts accepted for publication by peer-review journals. It is known that studies with certain 'favourable characteristics' have an increased likelihood of acceptance for publication, such as prospective study design, multiple sites, and notable authors.
Feasibility of the pre-operative measurement of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and respiratory mechanics to predict respiratory outcomes in children undergoing general anaesthesia
Peri-operative respiratory adverse events remain a major cause of morbidity and mortality in children undergoing general anaesthesia; those with asthma are at higher risk. The aim of this feasibility study was to determine whether pre-operative measurements of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and the forced oscillation technique are feasible in children, and to explore whether these measurements can predict peri-operative respiratory adverse events.
Topical Lidocaine During Airway Manipulation in Pediatric Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Lidocaine is widely used in pediatric anesthesia for airway topicalization to modulate undesirable airway and circulatory reflexes, yet its effectiveness remains unclear. Therefore, we aimed to perform a meta-analysis evaluating the impact of topical lidocaine on respiratory adverse events in children undergoing airway management.
Children's Anxiety in the Perioperative Environment: A Qualitative Exploration With Children, Parents and Staff at a Tertiary Paediatric Hospital
Perioperative anxiety is a common and distressing aspect of anaesthesia for many children, resulting in management challenges at the time of anaesthesia and potential physical and psychological adverse outcomes. We conducted this qualitative phenomenological study to explore the perspectives of children, parents and staff on perioperative anxiety in our institution. Planned recruitment was 20 each of children who had undergone elective anaesthesia, their parents and staff.
Health literacy scale for English-speaking children: translation and validation of the HLS-Child-Q15-EN
To translate and validate the HLS-Child-Q15, a relatively short questionnaire for assessing health literacy in children originally validated in German, into English to make it accessible to a large population of English-speaking children.
Current post-tonsillectomy analgesia practices among Australian and New Zealand anesthetists, and opinions on non-opioid alternatives
Children experience significant pain following extracapsular tonsillectomy surgery, and while opioids are often prescribed to treat this, clinicians may be wary of their adverse side effects, leading to variation in practice. There is a need for improved post-tonsillectomy pain management in children.
A qualitative exploration of the phenomenology of pain in children to inform pain assessment methods
Pain is a common experience associated with healthcare for children, who often recall it as the worst part of hospitalisation. Several factors make assessment of pain more challenging in children. Families have previously identified the development of improved tools to assess pain in children as a key priority. We therefore sough to investigate the nature of this experience from the perspective of children and their parents to inform the development of such tools.
Current Practices and Priorities of Anesthetists and Consumers for Infants Undergoing Inguinal Hernia Surgery
There is a paucity of data on the chosen anesthesia management for infant inguinal hernia surgery. We aimed to characterize self-reported anesthetic practice in Australia and New Zealand. We also aimed to identify the outcomes that matter to both anesthetists and to parents and carers.
Association of preoperative nocturnal hypoxaemia nadir and fentanyl ventilatory sensitivity in children with obstructive sleep apnoea undergoing general anaesthesia
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) has been thought to increase the risk of respiratory depression from opioids. The primary aim of this study was to assess whether preoperative hypoxaemia by sleep study pulse oximetry imparts greater opioid sensitivity.
Incidence of cognitive errors in difficult airway management: an inference human factors study from the Pediatric Difficult Intubation Registry
Cognitive errors are known contributors to poor decision-making in healthcare. However, their incidence and extent of their contribution to negative outcomes during difficult airway management are unknown. We aimed to identify cognitive errors during paediatric difficult airway management using data from the Pediatric Difficult Intubation (PeDI) registry, to determine patient and clinician factors associated with these errors, and their contribution to complications.
Quantitative electroencephalogram and machine learning to predict expired sevoflurane concentration in infants
Processed electroencephalography (EEG) indices used to guide anesthetic dosing in adults are not validated in young infants. Raw EEG can be processed mathematically, yielding quantitative EEG parameters (qEEG). We hypothesized that machine learning combined with qEEG can accurately classify expired sevoflurane concentrations in young infants. Knowledge from this may contribute to development of future infant-specific EEG algorithms.
Impact of honey on post-tonsillectomy pain in children (BEE PAIN FREE Trial): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised controlled trial*
Tonsillectomy, a common childhood surgery, is associated with difficult postoperative recovery. Previous reviews provided low-grade evidence that honey may improve recovery. The BEE PAIN FREE study investigated whether honey alongside multimodal analgesia improved the recovery trajectory in children following tonsillectomy.
Pediatric Endotracheal Tube Cuff Management at Altitude: Implications for Aeromedical Retrieval and Other Austere Environments
Children are sometimes transported via fixed or rotary wing aircraft for medical care. If they are intubated with a cuffed endotracheal tube (ETT), changes in environmental pressure during transport can alter cuff pressure. Cuff management in this setting varies widely by region and by organization. In this historical review, we sought to delineate the evolution of ETT cuff management in children undergoing aeromedical retrieval in order to progress the field toward an optimum strategy in the future.
Patient and carer priorities for research and clinical care of children with Down syndrome
Down syndrome, the most common genetic disorder, is caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. We identified the top 10 patient and carer research priorities for children with Down syndrome.
Comparing videolaryngoscopy and flexible bronchoscopy to rescue failed direct laryngoscopy in children: a propensity score matched analysis of the Pediatric Difficult Intubation Registry
Flexible bronchoscopy is the gold standard for difficult airway management. Clinicians are using videolaryngoscopy increasingly because it is perceived to be easier to use with high success rates. We conducted this study to compare the success rates of the two techniques when used after failed direct laryngoscopy in children with difficult tracheal intubations.
Awake Supraglottic Airway Placement in Pediatric Patients for Airway Obstruction or Difficult Intubation: Insights From an International Airway Registry (PeDI)
Small case series have described awake supraglottic airway placement in infants with significant airway obstruction and difficult intubations. We conducted this study to determine outcomes when supraglottic airways were placed in awake children enrolled in the international Pediatric Difficult Intubation Registry including success of ventilation, success of tracheal intubation, and complications.
Chewing gum to treat postoperative nausea and vomiting in female patients: a multicenter randomized trial
Postoperative nausea and vomiting is common after general anesthesia, with consequences for patient outcomes, satisfaction with care, and healthcare costs. The aim was to compare a new treatment, chewing gum, with a widely used intravenous agent, ondansetron, to treat postoperative nausea and vomiting in female patients in the postanesthesia care unit.
The future of paediatric obstructive sleep apnoea assessment: Integrating artificial intelligence, biomarkers, and more
Assessing obstructive sleep apnoea in children involves various methodologies, including sleep studies, nocturnal oximetry, and clinical evaluations. Previous literature has extensively discussed these traditional methods.
Airborne personal protective equipment availability and preparedness in Australian and New Zealand intensive care units: A point prevalence survey
Personal protective equipment is essential to protect healthcare workers when exposed to aerosol-generating procedures in patients with airborne respiratory pathogens.
Assessing the Use and Acceptability of Virtual Reality to Assist Coping in Children Undergoing Clinical Procedures
Virtual reality is used as a distraction tool during medical procedures that can cause anxiety and pain. We assessed the usefulness, engagement, value and feasibility of virtual reality to help children cope with routine clinical procedures.
Short-term outcomes in infants following general anesthesia with low-dose sevoflurane/dexmedetomidine/remifentanil versus standard dose sevoflurane (The TREX trial)
The Trial Remifentanil DEXmedetomidine trial aimed to determine if, in children < 2 years old, low-dose sevoflurane/dexmedetomidine/remifentanil anesthesia is superior to standard dose sevoflurane anesthesia in terms of global cognitive function at 3 years of age.
Net Promoter Score Model for Evaluating Paediatric Medicine Acceptability: Validation and Feasibility Study
Medicine acceptability is crucial for paediatric drug development, yet its assessment remains challenging due to the multifaceted nature of sensory attributes like taste, smell, and mouthfeel. Traditional methods of acceptability evaluation often involve complex questionnaires and lack standardisation, leading to difficulties in a comparative analysis across studies.
Caudal block, high flow oxygen insufflation and dexmedetomidine sedation for inguinal hernia surgery in infants—A prospective evaluation of an alternative anesthesia technique
Inguinal hernia repair is the most common operation in infants, with well recognized anesthetic and perioperative risks. The aim was to investigate if the combination of caudal block, high-flow nasal oxygen insufflation and intravenous dexmedetomidine sedation is suitable for infants undergoing inguinal hernia surgery.
Patient-related factors impact the implementation of inpatient antibiotic allergy delabeling
The clinical consequences of an antibiotic allergy label are detrimental, impacting health care delivery and patient outcomes. We assessed hospital inpatients with intent to offer free antibiotic allergy labeling assessment within a randomized controlled trial. We sought to determine the feasibility of establishing an adult antibiotic allergy delabeling service in a Western Australian tertiary public hospital.
Mode of delivery and behavioral and neuropsychological outcomes in children at 10 years of age
Previous studies have reported that mode of delivery, particularly cesarean delivery is associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes in children. This study evaluates behavioral and neuropsychological test scores in children based on mode of delivery.
Information overload and parental perspectives on information provided to parents/carers of paediatric patients undergoing elective surgical procedures
When parents are expected to play a significant role in the management of their children's health perioperatively, information overload for parents could have particularly detrimental consequences. Our study investigated information communication and overload in 380 parents of children undergoing any elective surgical procedure at our institution.
Propofol, Anesthesia, and Neurocognitive Outcomes in Patients with Pediatric Leukemia: Are We Missing the Forest for the Trees?
Preoperative preparation of children with upper respiratory tract infection: a focussed narrative review
This review summarises the current evidence for the perioperative preparation in children with upper respiratory tract infections (URTI), including COVID-19 infection. URTI, including COVID-19 infection, are common and frequent in children who present for elective surgery. Children with URTI are at increased risk of perioperative respiratory adverse events.
3-Dimensional Virtual Reality Versus 2-Dimensional Video for Distraction during the Induction of Anesthesia in Children to Reduce Anxiety: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Preoperative anxiety is common in children. It can contribute to negative experiences with anesthetic induction and may cause adverse physiological and psychological effects. Virtual reality (VR) and electronic tablet devices are 2 audiovisual distraction tools that may help to reduce anxiety and enhance the preoperative experience. This study aimed to compare the use of an immersive 3-dimensional (3D) VR to 2-dimensional (2D) video on anxiety in children during induction of general anesthesia.
Comparing Skin and Serum Testing to Direct Challenge Outcomes in Children With beta-Lactam Allergies
There is a scarcity of prospective studies investigating the relative roles of skin prick and intradermal testing, serum specific IgE, and extended oral challenges in diagnosing children with reported β-lactam allergies.
The Development of a Chocolate-Based Chewable Tablet of Prednisolone—Enhancing the Palatability of Steroids for Pediatric Use
Oral liquid prednisolone medications have poor acceptance among paediatric patients due to ineffective masking of the bitterness taste of prednisolone. This study aimed to develop a child-friendly prednisolone tablet using a patented chewable chocolate-based delivery system previously applied successfully to mask the bitterness tastes of midazolam and tramadol.
Rebooting the anal sphincter: A retrospective cohort of children with intractable constipation receiving intrasphincteric botox injections
Chronic childhood constipation is a common problem that severely impacts quality of life. Recently, the efficacy of intrasphincteric botulinum toxin (botox) injection in breaking the cycle of constipation has been demonstrated. The current study aims to investigate response rate to treatment, symptom and examination finding associations, and identify associations between patient characteristics and outcome.
Airway management in neonates and infants: Recommendations according to the ESAIC/BJA guidelines
Securing an airway enables the oxygenation and ventilation of the lungs and is a potentially life-saving medical procedure. Adverse and critical events are common during airway management, particularly in neonates and infants. The multifactorial reasons for this include patient-dependent, user-dependent and also external factors.
Effect of different lung recruitment strategies and airway device on oscillatory mechanics in children under general anaesthesia
Atelectasis has been reported in 68 to 100% of children undergoing general anaesthesia, a phenomenon that persists into the recovery period. Children receiving recruitment manoeuvres have less atelectasis and fewer episodes of oxygen desaturation during emergence. The optimal type of recruitment manoeuvre is unclear and may be influenced by the airway device chosen.
Jet versus vibrating mesh nebulizer for tobramycin aerosol in spontaneously breathing children with tracheostomies: A simulation study
Tracheostomy tubes act as foreign bodies, predisposing the surrounding airway to respiratory infections. Initial treatment for infections is topical - nebulized tobramycin - although guidelines for standardized treatment are lacking.
The use of honey in the perioperative care of tonsillectomy patients-A narrative review
Tonsillectomy is one of the most common surgical procedures in childhood. While generally safe, it often is associated with a difficult early recovery phase with poor oral intake, dehydration, difficult or painful swallowing, postoperative bleeding, infection and/or otalgia.
High-flow nasal oxygen for children's airway surgery to reduce hypoxaemic events: a randomised controlled trial
Tubeless upper airway surgery in children is a complex procedure in which surgeons and anaesthetists share the same operating field. These procedures are often interrupted for rescue oxygen therapy.
Behavioural and neuropsychological outcomes in children exposed in utero to maternal labour epidural analgesia
Recent studies report conflicting results regarding the relationship between labour epidural analgesia (LEA) in mothers and neurodevelopmental disorders in their offspring. We evaluated behavioural and neuropsychological test scores in children of mothers who used LEA.
Difficult intubation in syndromic versus nonsyndromic forms of micrognathia in children
We investigated how syndromic versus nonsyndromic forms of micrognathia impacted difficult intubation outcomes in children. Primary outcome was the first-attempt success rate of tracheal intubation, secondary outcomes were number of intubation attempts and complications. We hypothesized that syndromic micrognathia would be associated with lower first-attempt success rate.
Patient positioning and its impact on perioperative outcomes in children: A narrative review
Patient positioning interacts with a number of body systems and can impact clinically important perioperative outcomes. In this educational review, we present the available evidence on the impact that patient positioning can have in the pediatric perioperative setting. A literature search was conducted using search terms that focused on pediatric perioperative outcomes prioritized by contemporary research in this area.
Flexible bronchoscopy insufflated and high-flow nasal oxygen pilot trial (BUFFALO protocol pilot trial)
Hypoxaemia occurs in approximately 30% of children during anaesthesia for flexible bronchoscopy. High-flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) can prolong safe apnoea time and be used in children with abnormal airways. During flexible bronchoscopy, there is limited evidence if HFNO confers advantages over current standard practice in avoiding hypoxaemia. The aim is to investigate feasibility of HFNO use during anaesthesia for flexible bronchoscopy to reduce frequency of rescue oxygenation and hypoxaemia.
Airway management in the paediatric difficult intubation registry: a propensity score matched analysis of outcomes over time
The Paediatric Difficult Intubation Collaborative identified multiple attempts and persistence with direct laryngoscopy as risk factors for complications in children with difficult tracheal intubations and subsequently engaged in initiatives to reduce repeated attempts and persistence with direct laryngoscopy in children. We hypothesised these efforts would lead to fewer attempts, fewer direct laryngoscopy attempts and decrease complications.
Jelly snakes to reduce early postoperative vomiting in children after adenotonsillectomy: The randomized controlled snakes trial
Despite the use of dual antiemetic agents, postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) occurs in an unacceptably large number of patients post-tonsillectomy. There has been increased interest in alternative and non-pharmacological treatments for PONV e.g., chewing gum. We investigated if chewing a large confectionary jelly snake had prophylactic antiemetic effects postoperatively in young children.
Airway management in neonates and infants: European Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care and British Journal of Anaesthesia joint guidelines
Airway management is required during general anaesthesia and is essential for life-threatening conditions such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Evidence from recent trials indicates a high incidence of critical events during airway management, especially in neonates or infants. It is important to define the optimal techniques and strategies for airway management in these groups.
Predicting obstructive sleep apnoea and perioperative respiratory adverse events in children: role of upper airway collapsibility measurements
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and perioperative respiratory adverse events are significant risks for anaesthesia in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy. Upper airway collapse is a crucial feature of OSA that contributes to respiratory adverse events. A measure of upper airway collapsibility to identify undiagnosed OSA can help guide perioperative management. We investigated the utility of pharyngeal closing pressure for predicting OSA and respiratory adverse events.
Early life predictors of obstructive sleep apnoea in young adults: Insights from a longitudinal community cohort (Raine study)
Early-life obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) predictors are unavailable for young adults. This study identifies early-life factors predisposing young adults to OSA.
Perioperative steroid prophylaxis for adrenal insufficiency, a single-centre experience
Performance Accuracy of Wrist-Worn Oximetry and Its Automated Output Parameters for Screening Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) increases the risk of perioperative adverse events in children. While polysomnography remains the reference standard for OSA diagnosis, oximetry is a valuable screening tool. The traditional practice is the manual analysis of desaturation clusters derived from a tabletop device using the McGill oximetry score. However, automated analysis of wearable oximetry data can be an alternative. This study investigated the accuracy of wrist-worn oximetry with automated analysis as a preoperative OSA screening tool.
Early life predictors of obstructive sleep apnoea in young adults: Insights from a longitudinal community cohort (Raine study)
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) increases the risk of perioperative adverse events in children. While polysomnography (PSG) remains the reference standard for OSA diagnosis, oximetry is a valuable screening tool. The traditional practice is the manual analysis of desaturation clusters derived from a tabletop device using the McGill oximetry score. However, automated analysis of wearable oximetry data can be an alternative. This study investigated the accuracy of wrist-worn oximetry with automated analysis as a preoperative OSA screening tool.
Taste-Masked Flucloxacillin Powder Part 2: Formulation Optimisation Using the Mixture Design Approach and Storage Stability
Flucloxacillin is prescribed to treat skin infections but its highly bitter taste is poorly tolerated in children. This work describes the application of the D-optimal mixture experimental design to identify the optimal component ratio of flucloxacillin, Eudragit EPO and palmitic acid to prepare flucloxacillin taste-masked microparticles that would be stable to storage and would inhibit flucloxacillin release in the oral cavity while facilitating the total release of the flucloxacillin load in the lower gastrointestinal tract.
A review of pediatric fasting guidelines and strategies to help children manage preoperative fasting
Fasting for surgery is a routine step in the preoperative preparation for surgery. There have however been increasing concerns with regard to the high incidence of prolonged fasting in children, and the subsequent psycho-social distress and physiological consequences that this poses.
Difficult or impossible facemask ventilation in children with difficult tracheal intubation: a retrospective analysis of the PeDI registry
Difficult facemask ventilation is perilous in children whose tracheas are difficult to intubate. We hypothesised that certain physical characteristics and anaesthetic factors are associated with difficult mask ventilation in paediatric patients who also had difficult tracheal intubation.
Perioperative management of infant inguinal hernia surgery; a review of the recent literature
Inguinal hernia surgery is one of the most common electively performed surgeries in infants. The common nature of inguinal hernia combined with the high-risk population involving a predominance of preterm infants makes this a particular area of interest for those concerned with their perioperative care. Despite a large volume of literature in the area of infant inguinal hernia surgery, there remains much debate amongst anesthetists, surgeons and neonatologists regarding the optimal perioperative management of these patients.
Patient and Process Outcomes among Pediatric Patients Undergoing Appendectomy during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An International Retrospective Cohort Study
COVID-19 forced healthcare systems to make unprecedented changes in clinical care processes. The authors hypothesized that the COVID-19 pandemic adversely impacted timely access to care, perioperative processes, and clinical outcomes for pediatric patients undergoing primary appendectomy.
Efficacy of a hybrid technique of simultaneous videolaryngoscopy with flexible bronchoscopy in children with difficult direct laryngoscopy in the Pediatric Difficult Intubation Registry
Children with difficult tracheal intubation are at increased risk of severe complications, including hypoxaemia and cardiac arrest. Increasing experience with the simultaneous use of videolaryngoscopy and flexible bronchoscopy (hybrid) in adults led us to hypothesise that this hybrid technique could be used safely and effectively in children under general anaesthesia.
The role of WhatsApp™ in pediatric difficult airway management: A study from the PeDI Collaborative
Management of the pediatric difficult airway can present unique clinical challenges. The Pediatric Difficult Intubation Collaborative (PeDI-C) is an international collaborative group engaging in quality improvement and research in children with difficult airways. The PeDI-C established a WhatsApp™ group to facilitate real-time discussions around the management of the difficult airway in pediatric patients.
The influence of the COVID pandemic on the management of URTI in children
The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on paediatric anaesthesia research as evidenced by the contrasting recruitment experiences of centres in Australia and Scotland
Beta Agonists for Prevention of Respiratory Adverse Events in Children Undergoing Adenotonsillectomy: Long-Acting, Short Acting, or Not Acting
Adenotonsillectomy is one of the most common surgical interventions in children, and while generally safe, it is associated with a risk of significant adverse events. In this issue, Kim et al report a prospective randomized controlled study comparing preoperative use of a tulobuterol (longacting beta agonist) dermal patch with placebo on the incidence of perioperative respiratory adverse events (PRAEs) in children undergoing adenotonsillectomy.
The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on paediatric anaesthesia research as evidenced by the contrasting recruitment experiences of centres in Australia and Scotland
At two hospitals in Western Australia, we conducted a prospective, open-label, randomised, controlled trial of 240 patients undergoing tonsillectomy to investigate the effect of chewing a confectionery jelly snake on postoperative nausea and vomiting. The results were published in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain Medicine. Recruitment for this study was completed uneventfully between July 2018 and August 2019.
Kids Voices, the perioperative experience of emergency surgery from children's perspectives: A qualitative study
The study aimed to better understand children's emergency perioperative experience, a little researched topic. Current literature shows discrepancies between child and adult perceptions for the same healthcare experience. Acquisition of knowledge from the child's perspective can be utilized to improve perioperative care.
Feasibility of upper airway collapsibility measurements in anesthetized children
Patients with a propensity for upper airway obstruction, including those with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), are vulnerable in the perioperative period. OSA is an increasingly common disorder in children and, when present, is associated with an increased risk of perioperative respiratory adverse events (PRAE),1 morbidity, and mortality. Therefore, identifying at-risk patients is vital to provide tailored perioperative anesthetic management.
Perioperative intravenous lidocaine use in children
Perioperative pain management impacts patient morbidity, quality of life, and hospitalization cost. In children, it impacts not only the child, but the whole family. Adjuncts for improved perioperative analgesia continue to be sought to minimize adverse side effects associated with opioids and for those in whom regional or neuraxial anesthesia is not suitable.
Direct versus video laryngoscopy with standard blades for neonatal and infant tracheal intubation with supplemental oxygen: a multicentre, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial
Tracheal intubation in neonates and infants is a potentially life-saving procedure. Video laryngoscopy has been found to improve first-attempt tracheal intubation success and reduce complications compared with direct laryngoscopy in children younger than 12 months.
Consumer research priorities for pediatric anesthesia and perioperative medicine
Consumer-driven research is increasingly being prioritized. Aim: Our aim was to partner with consumers to identify the top 10 research priorities for pediatric anesthesia and perioperative medicine. The ACORN (Anesthesia Consumer Research Network) was formed to collaborate with children and families across Australia.
Sedation versus General Anesthesia for Tracheal Intubation in Children with Difficult Airways: A Cohort Study from the Pediatric Difficult Intubation Registry
Sedated and awake tracheal intubation approaches are considered safest in adults with difficult airways, but little is known about the outcomes of sedated intubations in children. The primary aim of this study was to compare the first-attempt success rate of tracheal intubation during sedated tracheal intubation versus tracheal intubation under general anesthesia. The hypothesis was that sedated intubation would be associated with a lower first-attempt success rate and more complications than general anesthesia.
Anaesthesia related mortality data at a Tertiary Pediatric Hospital in Western Australia
Anaesthesia related mortality in paediatrics is rare. There are limited data describing paediatric anaesthesia related mortality. This study determined the anaesthesia related mortality at a Tertiary Paediatric Hospital in Western Australia.
The seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in children, Australia, November 2020 - March 2021
Remote after-care using smartphones: A feasibility study of monitoring children's pain with automated SMS messaging
Monitoring children's recovery postoperatively is important for routine care, research, and quality improvement. Although telephone follow-up is common, it is also time-consuming and intrusive for families. Using SMS messaging to communicate with families regarding their child's recovery has the potential to address these concerns. While a previous survey at our institution indicated that parents were willing to communicate with the hospital by SMS, data on response rates for SMS-based postoperative data collection is limited, particularly in pediatric populations.
Isoelectric Electroencephalography in Infants and Toddlers during Anesthesia for Surgery: An International Observational Study
Intraoperative isoelectric electroencephalography (EEG) has been associated with hypotension and postoperative delirium in adults. This international prospective observational study sought to determine the prevalence of isoelectric EEG in young children during anesthesia.
Penicillin allergy SHACK: Survey of hospital and community knowledge
Penicillin allergy accounts for the majority of all reported adverse drug reactions in adults and children. Foregoing first-line antibiotic therapy due to penicillin allergy label is associated with an increased prevalence of infections by resistant organisms and longer hospitalisation.
A randomised controlled trial of a novel tramadol chewable tablet: pharmacokinetics and tolerability in children
Tramadol is a bitter atypical opioid analgesic drug and is prescribed to treat postoperative pain in children. However, in many countries there is no licensed paediatric tramadol formulation available. We have formulated a novel chewable chocolate-based drug delivery system for the administration of tramadol to children.
N95-masks to protect health care workers: Is the new fast fit-test protocol cutting corners?
Primum non nocere (“first do no harm”) with oxygen therapy
The “IKEA-effect” and modern anesthesia machines
Someday we’ll look back on this, and it will all seem funny. The lung and ventilation special issue 2030 and beyond
The secret to longevity is to keep breathing (Sophie Tucker)
Developmental respiratory physiology
Various developmental aspects of respiratory physiology put infants and young children at an increased risk of respiratory failure, which is associated with a higher rate of critical incidents during anesthesia.
Risk assessment and optimization strategies to reduce perioperative respiratory adverse events in pediatric anesthesia—Part 1 patient and surgical factors
Pediatric surgery cases are increasing worldwide. Within pediatric anesthesia, perioperative respiratory adverse events are the most common precipitant leading to serious complications.
Clinical utility of preoperative pulmonary function testing in pediatrics
Perioperative respiratory adverse events pose a significant risk in pediatric anesthesia, and identifying these risks is vital. Traditionally, this is assessed using history and examination. However, the perioperative risk is multifactorial, and children with complex medical backgrounds such as chronic lung disease or obesity may benefit from additional objective preoperative pulmonary function tests.
Aerosolized drug delivery in awake and anesthetized children to treat bronchospasm
Bronchospasm is a common respiratory adverse event in pediatric anesthesia. First-line treatment commonly includes inhaled salbutamol. This review focuses on the current best practice to deliver aerosolized medications to awake as well as anesthetized pediatric patients and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of various administration techniques.
Anesthetic considerations in children with asthma
Due to the high prevalence of asthma and general airway reactivity, anesthesiologists frequently encounter children with asthma or asthma-like symptoms. This review focuses on the epidemiology, the underlying pathophysiology, and perioperative management of children with airway reactivity, including controlled and uncontrolled asthma.
COVID-19 implications for pediatric anesthesia: Lessons learnt and how to prepare for the next pandemic
COVID-19 is mainly considered an “adult pandemic,” but it also has strong implications for children and consequently for pediatric anesthesia. Despite the lethality of SARS-CoV-2 infection being directly correlated with age, children have equally experienced the negative impacts of this pandemic.
Atelectasis and lung recruitment in pediatric anesthesia: An educational review
General anesthesia is associated with development of pulmonary atelectasis. Children are more vulnerable to the development and adverse effects of atelectasis. We review the physiology and risk factors for the development of atelectasis in pediatric patients under general anesthesia.
Impact of airway and a standardized recruitment maneuver on CT chest imaging quality in a pediatric population: A retrospective review
When performing computerized tomography chest imaging in children, obtaining high quality, motion-free images is important in the accurate diagnosis of underlying pathology. General anesthesia is associated with the development of atelectasis, which can impair accurate diagnosis by obscuring or altering the appearance of the lung parenchyma or airways.
Parents' perspectives towards paediatric confectionary masked medications: a qualitative study
The availability of age-appropriate, taste-masked oral solid medications for the paediatric population is currently inadequate. We have developed a novel chocolate-based drug delivery platform to taste-mask bitter drugs commonly utilised in the hospital setting, but there is limited evidence regarding parent's perspectives on these medications.
Complications associated with paediatric airway management during the COVID-19 pandemic: an international, multicentre, observational study
Respiratory adverse events in adults with COVID-19 undergoing general anaesthesia can be life-threatening. However, there remains a knowledge gap about respiratory adverse events in children with COVID-19. We created an international observational registry to collect airway management outcomes in children with COVID-19 who were having a general anaesthetic.
Procedural anesthesia and sedation for children undergoing diagnostic and medical procedures — A review of postprocedural pain, nausea, and vomiting by questionnaire-based survey
Sedation and anesthesia are widely used to relieve pain and ensure cooperation during elective diagnostic and medical procedures in the pediatric population. However, there is currently limited evidence about the recovery trajectory following deep sedation or general anesthesia for such procedures in children.
Comparison of two measures of behavior change in children after day surgery
A contemporary, well-validated instrument for the measurement of behavior change in children after general anesthesia is lacking. The Post Hospitalization Behavior Questionnaire for Ambulatory Surgery (PHBQ-AS) has been developed as an updated version of the original Post Hospitalization Behavior Questionnaire (PHBQ) to better reflect the current patient population and modern anesthetic practices.
Risk assessment and optimization strategies to reduce perioperative respiratory adverse events in Pediatric Anesthesia—Part 2: Anesthesia-related risk and treatment options
Perioperative respiratory adverse events are the most common cause of critical events in children undergoing anesthesia and surgery. While many risk factors remain unmodifiable, there are numerous anesthetic management decisions which can impact the incidence and impact of these events, especially in at-risk children.
Lung ultrasound and atelectasis—The devil is in the details
Without training, they lacked knowledge. Without knowledge, they lacked confidence. Without confidence, they lacked victory (Julius Caesar)
Error traps in pediatric difficult airway management
Difficult airway management in children is associated with significant morbidity. This narrative review on error traps in airway management aims to highlight the common pitfalls and proposes solutions to optimize best practices for pediatric difficult airway management. We have categorized common errors of pediatric difficult airway management into three main error traps.
"Cannot intubate, cannot oxygenate": A novel 2-operator technique for cannula tracheotomy in an infant animal model-a feasibility study
Evidence regarding optimal management of the "Cannot Intubate, Cannot Oxygenate" (CICO) scenario in infants is scarce. When inserting a transtracheal cannula for front of neck access direct aspiration to confirm intratracheal location is standard practice.
Kids voices: Exploring children's perspective of tonsillectomy surgery
Prenatal Exposure to General Anesthesia and Childhood Behavioral Deficit
Exposure to surgery and anesthesia in early childhood has been found to be associated with an increased risk of behavioral deficits. While the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has warned against prenatal exposure to anesthetic drugs, little clinical evidence exists to support this recommendation.
Prescribing in a pediatric hospital setting – Lost in translation?
To determine parental understanding of directions on common pediatric prescription pharmacy labels and to identify enablers and barriers that affect interpretation of these labels.
HPLC-UV assay of tramadol and O-desmethyltramadol in human plasma containing other drugs potentially co-administered to participants in a paediatric population pharmacokinetic study
Multimodal analgesia is employed in paediatric pain management to maximise analgesia and minimise side effects. Tramadol is dosed at 1–1.5 mg/kg to treat severe pain in children but the assay for tramadol in plasma samples for pharmacokinetic and toxicology studies does not often consider concurrently administered medications.
Prior administration of chocolate improves the palatability of bitter drugs: The Choc-with-Med study
The paediatric population has a low adherence and acceptance rate of unpalatable medicines. This study aimed to determine whether eating chocolate immediately prior to drug administration would help to mask the bitter taste of a drug. The difference in taste masking efficacy between white, milk and dark chocolate was a secondary measure outcome.
Lessons from COVID-19: A reflection on the strengths and weakness of early consensus recommendations for pediatric difficult airway management during a respiratory viral pandemic using a modified Delphi method
The authors recognized a gap in existing guidelines and convened a modified Delphi process to address novel issues in pediatric difficult airway management raised by the COVID-19 pandemic. The Pediatric Difficult Intubation Collaborative, a working group of the Society for Pediatric Anesthesia, assembled an international panel to reach consensus recommendations on pediatric difficult airway management during the COVID-19 pandemic using a modified Delphi method.
Pediatric Airway Management in Times of COVID-19-a Review of the Evidence and Controversies
This review summarizes and provides a comprehensive narrative synthesis of the current evidence on pediatric airway management during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Peri-operative steroid management in the paediatric population
Patients with adrenal insufficiency are at risk of adrenal crisis, a potentially life-threatening emergency in the peri-operative period due to their attenuated ability to mount a cortisol response.
More than half of front-line healthcare workers unknowingly used an N95/P2 mask without adequate airborne protection: An audit in a tertiary institution
Front-line staff routinely exposed to aerosol-generating procedures are at a particularly high risk of transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. We aimed to assess the adequacy of respiratory protection provided by available N95/P2 masks to staff routinely exposed to aerosol-generating procedures.
A survey of the global impact of COVID-19 on the practice of pediatric anesthesia: A study from the pediatric anesthesia COVID-19 Collaborative Group
Pediatric anesthesiology has been greatly impacted by COVID-19 in the delivery of care to patients and to the individual providers. With this study, we sought to survey pediatric centers and highlight the variations in care related to perioperative medicine during the COVID-19 pandemic, including the availability of protective equipment, the practice of pediatric anesthesia, and economic impact.
Pediatric airway management
Children are at risk of severe hypoxemia in the perioperative period owing to their unique anatomy and physiology. Safe and effective airway management strategies are therefore key to the practice of pediatric anesthesia. The goal of this review is to highlight recent publications (2019-2021) aimed to advance pediatric airway safety and to highlight a proposed simple, pediatric-specific, universal framework to guide clinical practice.
An assessment of opioids on respiratory depression in children with and without obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is a risk factor for respiratory depression following opioid administration as well as opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Little is known on how obstructive sleep apnea status is associated with central ventilatory depression in pediatric surgical patients given a single dose of fentanyl.
Carbon dioxide monitoring in children—A narrative review of physiology, value, and pitfalls in clinical practice
Continuous capnography has been recognised as an essential monitoring device in all anesthetized patients, despite which airway device is in use, regardless of their location, as a measure to improve patient safety. Capnography is the non-invasive measurement of a sample of the exhaled carbon dioxide which has multiple clinical uses including as a method to confirm placement of a tracheal tube and/or to assess ventilation, perfusion and metabolism.
Prenatal Exposure to General Anesthesia and Childhood Behavioral Deficit
Exposure to surgery and anesthesia in early childhood has been found to be associated with an increased risk of behavioral deficits. While the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has warned against prenatal exposure to anesthetic drugs, little clinical evidence exists to support this recommendation. This study evaluates the association between prenatal exposure to general anesthesia due to maternal procedures during pregnancy and neuropsychological and behavioral outcome scores at age 10.
Gender Balance in Anesthesiology: Is a Change of Societal Mindset Needed?
With great interest, we are following the discussion on Speaker Gender Representation and Trends in Authorship. While it is indeed very popular and important to look at speaker representation, authorship, or board membership by gender, the underlying reasons for the unequal gender representation are not as easy to determine. Counting numbers on panels or boards may also not add up to real representation.
Perioperative pediatric tonsillectomy analgesia: A single-center review of practice and cost-effectiveness analysis
Tonsillectomy is one of the most common pediatric surgeries and results in considerable postoperative pain. Insufficiently managed pain is costly, risks physiological and psychological consequences with multi-modal analgesia widely recommended to minimize opioid-based agents. We determined adherence to multi-modal analgesia guidelines and assessed cost-effectiveness. We undertook a cross-sectional cohort study at a tertiary pediatric institution in Perth, Western Australia, retrospectively identifying selected patients undergoing tonsillectomy over two discrete periods of 6-week duration.
An observational study of hypoactive delirium in the post-anesthesia recovery unit of a pediatric hospital
Hypoactive delirium is present when an awake child is unaware of his or her surroundings, is unable to focus attention, and appears quiet and withdrawn. This condition has been well-described in the intensive care setting but has not been extensively studied in the immediate post-anesthetic period. The aim was to determine if hypoactive emergence delirium occurs in the recovery unit of a pediatric hospital, and if so, what proportion of emergence delirium is hypoactive in nature.
A comparison of videolaryngoscopy using standard blades or non-standard blades in children in the Paediatric Difficult Intubation Registry
The design of a videolaryngoscope blade may affect its efficacy. We classified videolaryngoscope blades as standard and non-standard shapes to compare their efficacy performing tracheal intubation in children enrolled in the Paediatric Difficult Intubation Registry.
The role of fit testing N95/FFP2/FFP3 masks: a narrative review
For healthcare workers performing aerosol-generating procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic, well fitted filtering facepiece respirators, for example, N95/FFP2 or N99/FFP3 masks, are recommended as part of personal protective equipment. In this review, we evaluate the role of fit checking and fit testing of respirators, in addition to airborne protection provided by respirators. Filtering facepiece respirators are made of material with sufficient high filter capacity to protect against airborne respiratory viruses.
Impact of a revised postoperative care plan on pain and recovery trajectory following pediatric tonsillectomy
A previous cohort of adenotonsillectomy patients at our institution demonstrated moderate-severe post-tonsillectomy pain scores lasting a median (range) duration of 6 (0-23) days and postdischarge nausea and vomiting affecting 8% of children on day 1 following surgery. In this subsequent cohort, we evaluate the impact of changes to our discharge medication and parental education on post-tonsillectomy pain and recovery profile.
The impact of surgical cancellations on children, families, and the health system in an Australian paediatric tertiary referral hospital
Reasons for elective surgery cancelations and their impact vary from one institution to another. Cancelations have emotional and financial implications for patients and their families. Our service has a particularly broad and geographically diverse patient population; hence, we sought to examine these impacts in our service.
Assessment of different techniques for the administration of inhaled salbutamol in children breathing spontaneously via tracheal tubes, supraglottic airway devices, and
Perioperative respiratory adverse events account for a third of all perioperative cardiac arrests, with bronchospasm and laryngospasm being most common. Standard treatment for bronchospasm is administration of inhaled salbutamol, via pressurized metered dose inhaler. There is little evidence on the best method of attaching the pressurized metered dose inhaler to the artificial airway during general anesthesia. The aim of this study is to investigate the best method to deliver aerosolized salbutamol via pressurized metered dose inhaler to the lungs of an anesthetized child.
Assessment of different techniques for the administration of inhaled salbutamol in children breathing spontaneously via tracheal tubes, supraglottic airway devices, and tracheostomies
Perioperative respiratory adverse events account for a third of all perioperative cardiac arrests, with bronchospasm and laryngospasm being most common. Standard treatment for bronchospasm is administration of inhaled salbutamol, via pressurized metered dose inhaler. There is little evidence on the best method of attaching the pressurized metered dose inhaler to the artificial airway during general anesthesia. The aim of this study is to investigate the best method to deliver aerosolized salbutamol via pressurized metered dose inhaler to the lungs of an anesthetized child.
Fit testing of N95 or P2 masks to protect health care workers
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and has many similarities to severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). While reported morbidity and mortality from COVID-19 are lower than from SARS and MERS, many health care workers have been infected (up to 15% of health care workers in Victoria).
Anaesthesia, pain and recovery profiles in children following dental extractions
The aim of this prospective cohort study was to describe the anaesthetic practices, rates of postoperative pain and the recovery trajectory of children having urgent dental extractions at our institution.
The plural of anecdote is not data, please mind the gap
The COVID-19 pandemic introduced challenges to everyone in society but particularly so to every aspect of medical practice. It is bewildering how quickly the profession has had to respond to rapidly changing clinical landscape. Our well-established methods involve collecting and analyzing data to generate an evidence base which is then disseminated and implemented into routine clinical practice.
What’s inside the box? Or shall we think outside the box?
With the deadly and highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 virus causing the COVID-19 pandemic, there is global concern about the danger of contaminating healthcare workers (HCW), particularly during airway management of infected patients.
Preoperative identification of children at high risk of obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea poses as an anesthetic challenge, and it is a well-known risk factor for perioperative adverse events
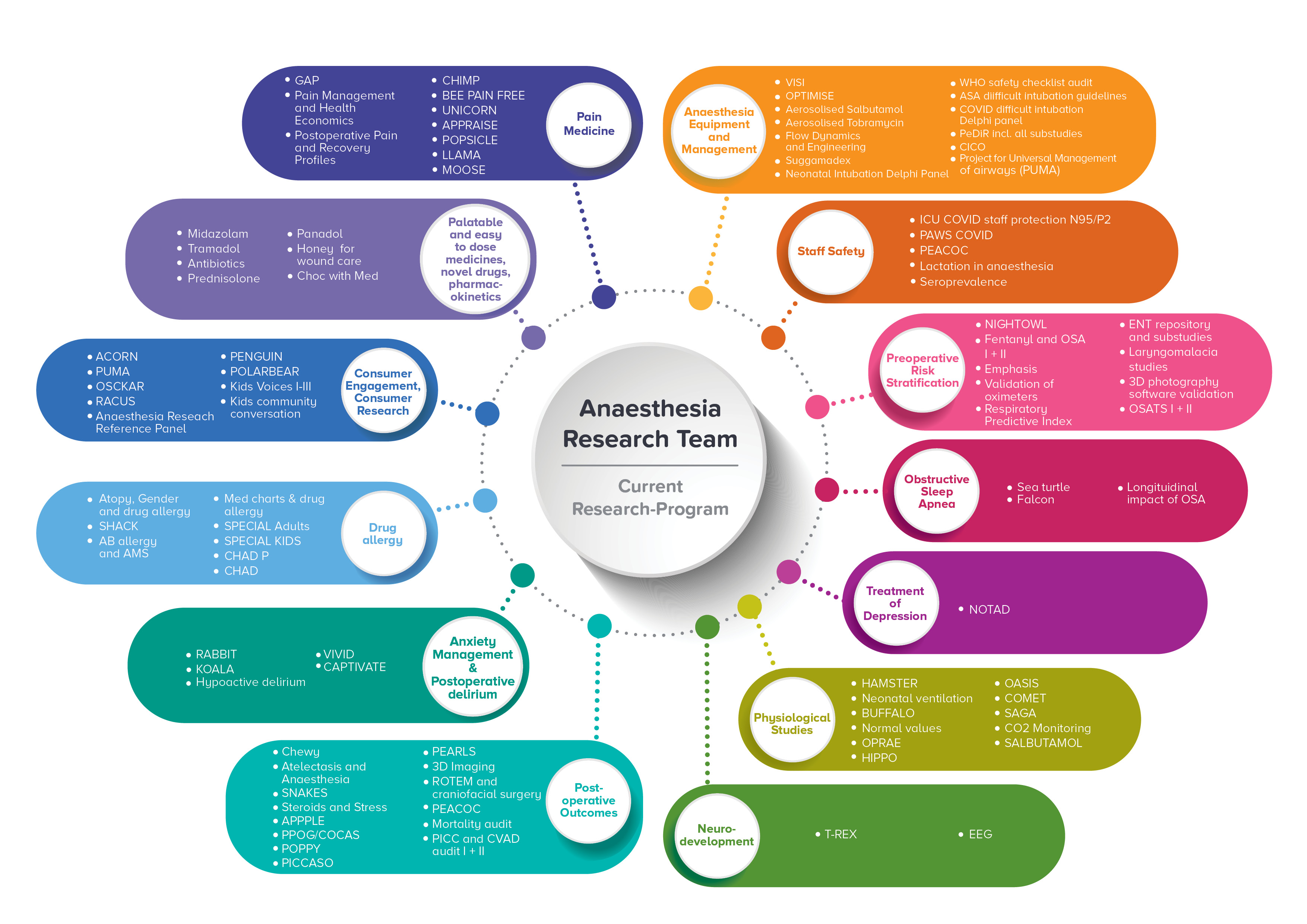
Projects
Education and Qualifications
• MD – University of Freiburg, Germany
• PhD- University of Szegad, Hungary
• FANZCA (Fellow of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists)- Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists
Awards/Honours
- 2010 - Raine Research Award for work regarding the prediction and prevention of respiratory complications.
- 2013 - Douglas Joseph Professorship, Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists, “A new prediction strategy to prevent respiratory complications in paediatric anaesthesia”
- 2016 - John Boyd Craig Research Award: Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists, "Palatable and chewable tramadol chocolate-based tablets for effective pain management in young"
- 2019 - University of Western Australia Health and Medical School Early-Mid Career Researcher Impact Award
- 2019 - Publication Award for an original journal article in the journal with the highest ranking by field for Von Ungern-Sternberg BS, Sommerfield D, Slevin L, Drake-Brockman TFE, Zhang G, Hall GL. Effect of Albuterol Premedication vs Placebo on the Occurrence of Respiratory Adverse Events in Children Undergoing Tonsillectomies: The REACT Randomized Clinical Trial. (JAMA Pediatrics). 2019;173(6):527-33.
- 2020 - Prime Minister’s Science Prizes shortlisted for the Frank Fenner Prize for Life Scientist of the Year
- 2021 - Premier’s Science Awards, Finalist for Scientist of the Year
- 2022 - Child and Adolescent Health Service Spirit of Innovation award
- 2022 - Inducted into the WA Women Hall of Fame
- 2022 - Australian Clinical Trials Alliance Consumer Engagement Prize, runner up for Bee Pain Free Study
- 2022 - Western Australian Young Tall Poppy Science Award 2022 and WA Tall Poppy of the Year
- University of Western Australia Medical School Excellence in Research 2022 Impact and Innovation Award
- 2023 - The Byron Kakulas Medal - acknowledging people who have had a transformational impact on the health of Western Australians
- 2023 - Prime Minister’s Science Prizes, shortlisted for the Frank Fenner Prize for Life Scientist of the Year
- 2023 - Premier’s Science Awards, Mid-Career Scientist of the Year
- 2023 - UWA Medical School Mid-Career Research Award
Active Collaborations
- Advisory Group member for the Project for Universal Management of Airways (PUMA) - international multidisciplinary group
- Expert international consultant for the revision of the Difficult Airway Guidelines for the SPA (Society of Pediatric Anesthesiology, USA)
- Western Australian representative on the Australasian Paediatric Perioperative Learning eHealthcare System
- Brain Research Anesthesia Infant Network (BRAIN)
- International Pediatric Perioperative Outcomes Group (PPOG)
- Core Group member of the Pediatric Difficult Airway Registry (PeDiR)
- External consultant to the ASA (American Society of Anesthesiology) difficult airway working group
- SPANZA (Society of Paediatric Anaesthesia in New Zealand and Australia) research collaboration
- Taskforce Member for the BJA/ESAIC Guidelines on Neonatal Airway management.
- Steering Committee Member for the BIG APPLE international study
- Steering Committee Member for OPTIMISE2 study
- Member of PARNet (Paediatric Anaesthesia Research Network, Europe)
- Steering Committee Member for the CRICKET international study
